Sunday, January 14, 2024 From rOpenSci (https://ropensci.org/blog/2024/01/14/runiverse-arm64/). Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under the CC-BY license.
🔗 Abstract / TLDR
R-universe now provides MacOS arm64 binaries for all R packages. This means that MacOS users on Apple Silicon hardware (aka M1/M2/M3) can install the very latest builds of any R package without the need for any compilation:
install.packages('arrow',
repos = c('https://apache.r-universe.dev', 'https://cloud.r-project.org'))
R-universe uses cross-compiling for arm64 binaries, though this should not make much of a difference for package authors and R users. Packages with C/C++/Fortran/Rust code are all supported.
🔗 Why cross compiling
Because GitHub Actions currently does not offer arm64 runners for OSS projects, the arm64 binaries are cross-compiled on the MacOS intel runners. The cross build environment is set up to mimic a native arm64 machine, such that most R packages do not need any modification to work. We found only a small number of packages with a buggy configure script that may need a fix to allow cross-compilation.
The r-universe workflow only builds arm64 binaries when needed, i.e. for packages that include compiled code (C/C++/Fortran/Rust). Packages that do not include any compiled code are portable by design, so for these packages the binaries built for MacOS on intel are served both in the x86_64 and arm64 cranlike repositories, without the need for an additional cross compile step.
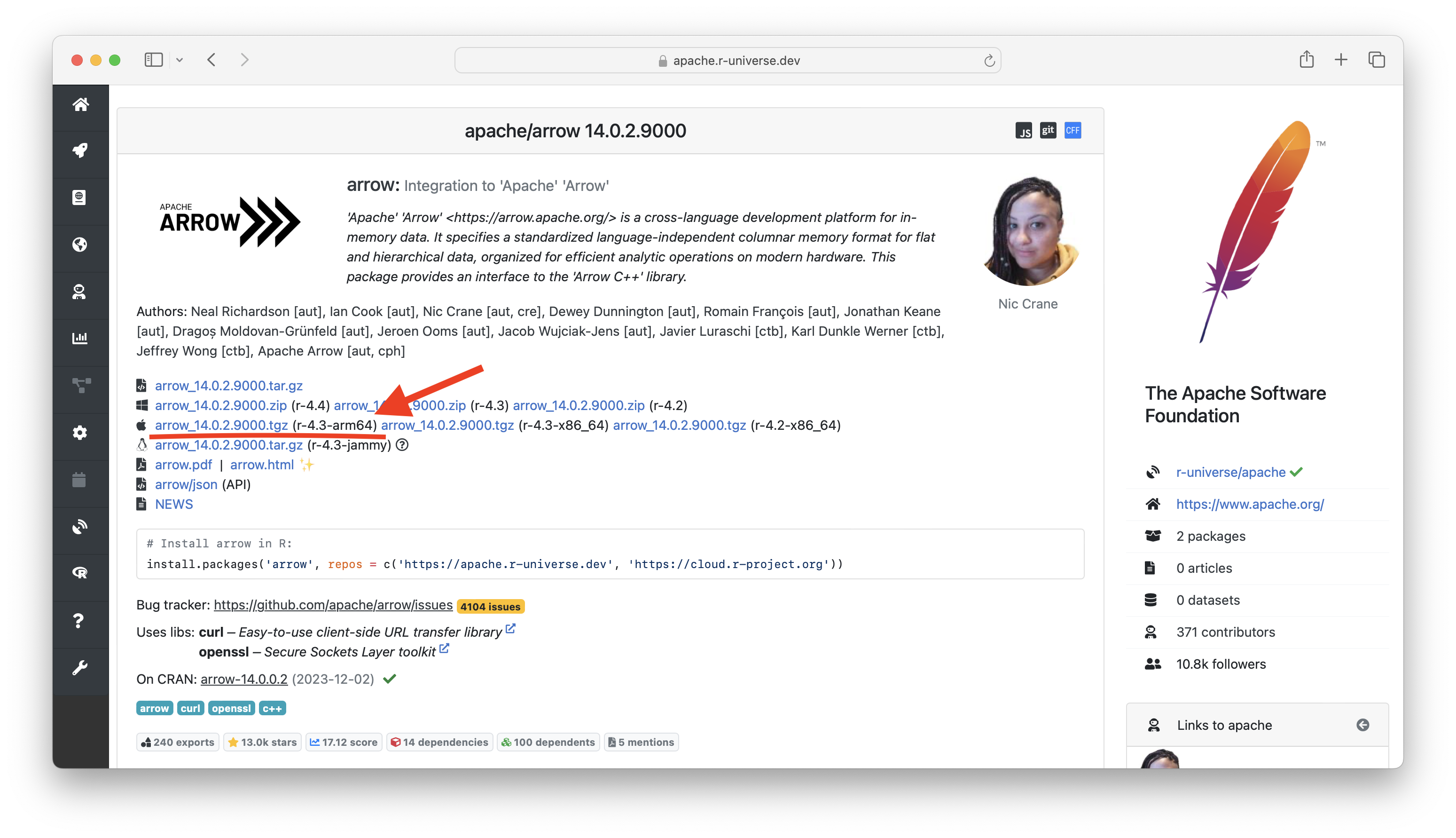
Just like CRAN, the r-universe package homepage shows a link to the r-4.3-x86_64 and r-4.3-arm64 binaries. Packages without compiled code have a r-4.3-any binary which is used for either architecture.
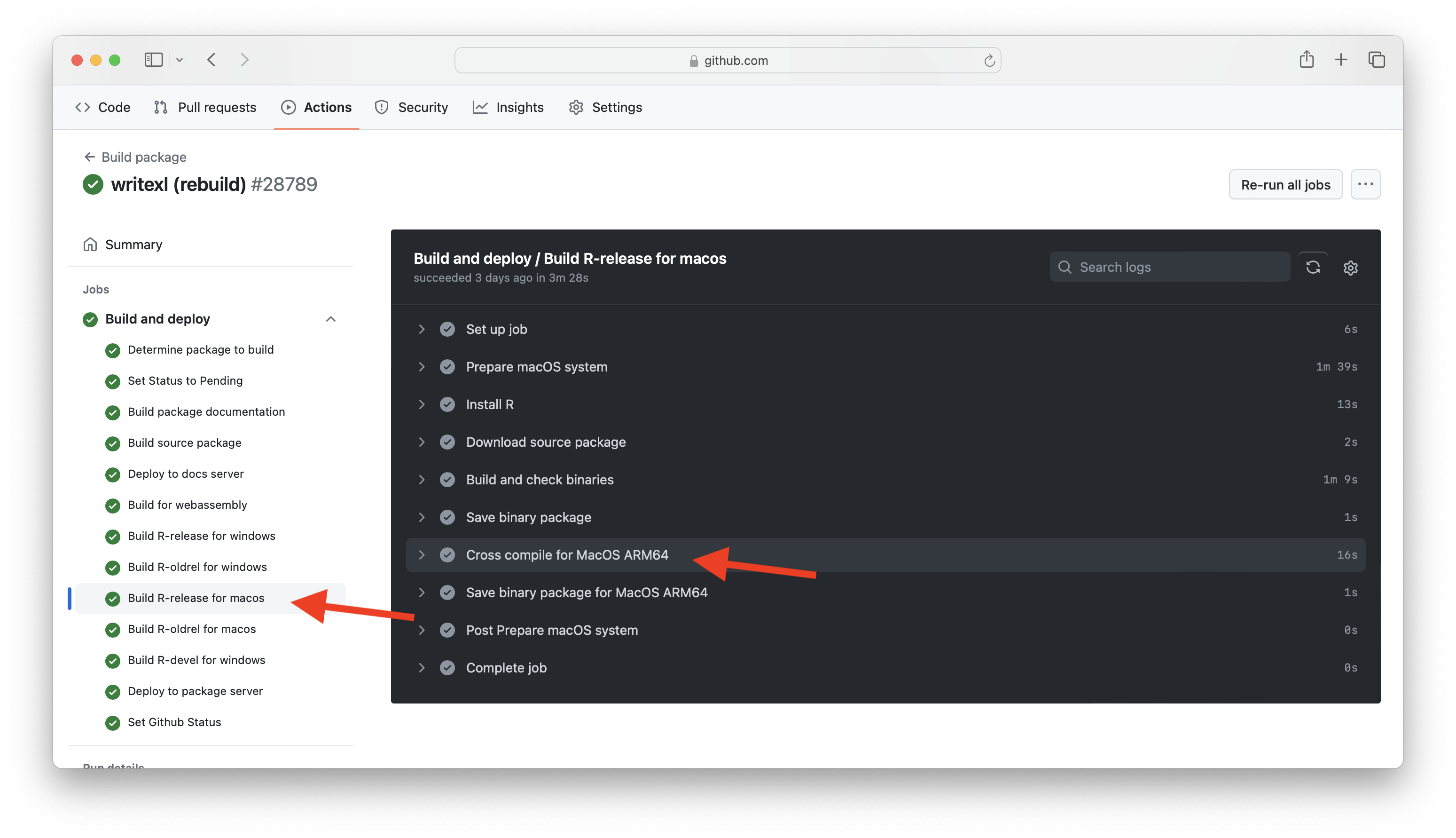
To have a look at the build logs, click on the little apple icon next to these links. Alternatively, you can use the /buildlog shortlink, for example https://apache.r-universe.dev/arrow/buildlog will take you to the latest arrow builds.
On this page you can find the arm64 build log specifically by expanding the r-release-macos job and then under the section “Cross Compile for MacOS ARM64”. If this section is disabled, it means it was skipped because this package does not have compiled code, and does not need cross compilation.
🔗 Some technical details
For those interested how the cross compilation is set up, here are the main ingredients:
- The standard MacOS Xcode toolchains are used to cross compile C/C++ code by passing the
-arch arm64flag to clang and clang++. - The universal gfortran 12.2 version from CRAN (thanks to Simon Urbanek) is used to cross compile fortran code, also by passing
gfortran -arch arm64. - The same collection of system libs used by CRAN is preinstalled in the build environment.
- R packages with a configure script are built with
--configure-args="--build=x86_64-apple-darwin20 --host=aarch64-apple-darwin20". These flags are needed by autoconf scripts, but other packages can use them as well. - The r-universe macos-cross workflow overrides some more files and variables to target arm64.
- We put some shell shims on the PATH to help packages that shell out to
unameorarchto determine the architecture. - A clever cargo shim is used to override the default cargo build target to
aarch64-apple-darwinand copy outputs to the expected directory after the build. - Packages are built with strict linking (without the
-undefined dynamic_lookupflag).
With this setup, almost any R package can be built in the cross environment exactly the same way they do on normal arm64 hardware. But if your package does not work and you need some help fixing it, please feel free to open an issue.
🔗 Universal binaries
Finally, some R packages download precompiled binaries for libraries too big or complicated to build on the fly. It is safest to distribute such libraries in the form of universal binaries which contain both the x86_64 and arm64 libs. This way your download script does not need to make any guesses about the target architecture it is building for: the same libs can be linked on either target.
Creating a universal binary can be done for both static and dynamic libraries and is really easy. If you have a x86_64 and arm64 version of libfoo.a you can glue them together with lipo:
lipo -create x86_64/libfoo.a arm64/libfoo.a -output universal/libfoo.a
And this new libfoo.a can be used when building either for intel or arm. Again if you need any help with this feel free to reach out.